Three Dimesional Reconstruction
In the domain of urban informatics, 3D reconstruction refers to the process of creating three-dimensional digital models of urban environments, such as buildings, streets, and entire cityscapes, using various data sources like photographs, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), or satellite imagery. This technology allows urban planners, researchers, and city officials to better understand, analyze, and visualize the complexities of urban spaces. To create these 3D models, data is collected from different perspectives, often using drones, street-level cameras, or even smartphones, and then processed with advanced algorithms. These models can represent not only the physical structure of a city but also incorporate other layers of information, such as traffic patterns, environmental data, or social activities. In urban informatics, 3D reconstruction serves multiple purposes, such as enhancing city planning, improving infrastructure development, supporting disaster management, and analyzing urban dynamics. By transforming real-world spaces into interactive, data-rich 3D models, it enables better decision-making and more informed strategies for sustainable urban development.
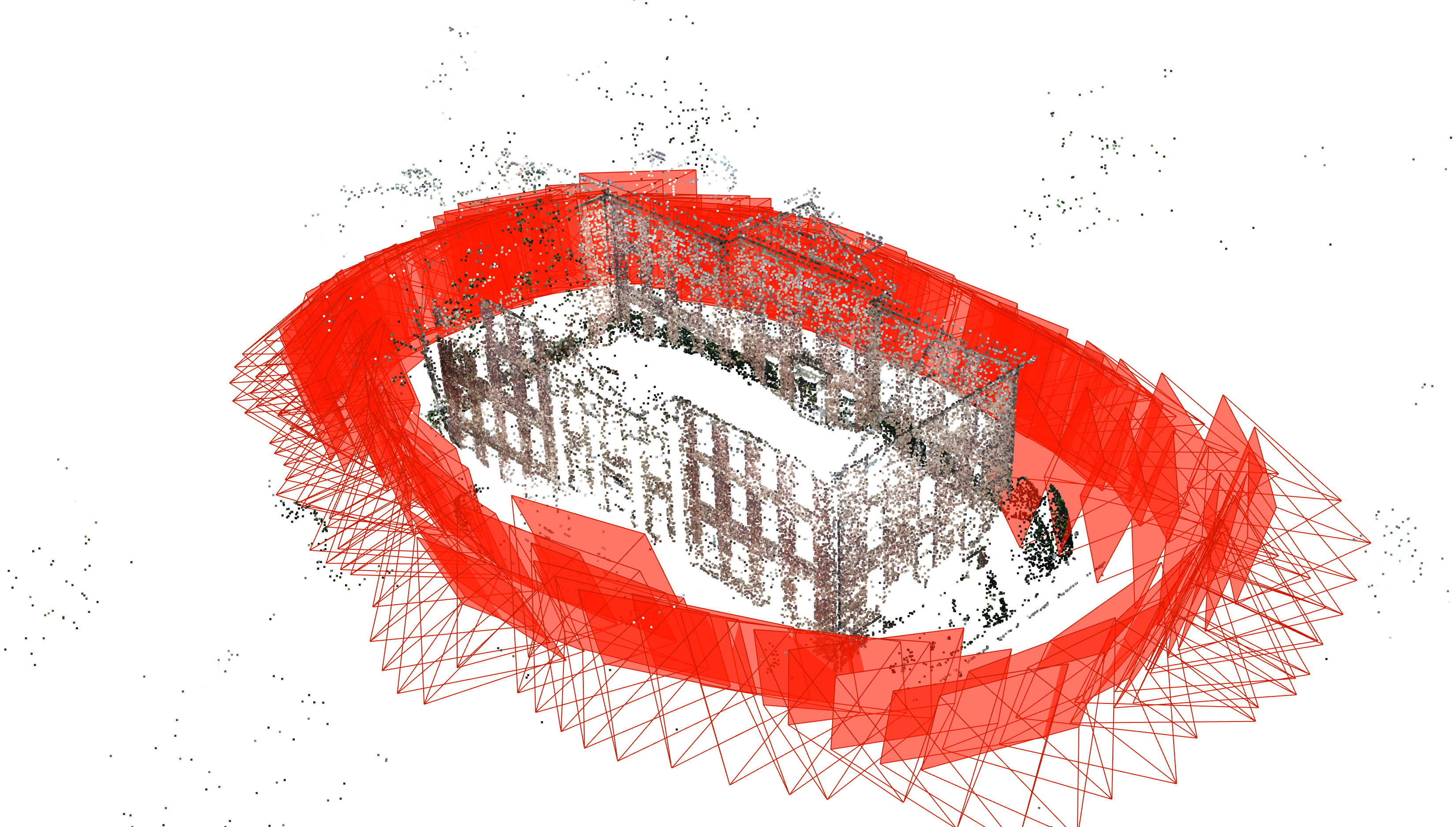
Figure 1: Example of reconstructing buildings from point clouds and camera images